What you need to know about electric bike motors
There are two popular types of electric bike motors. Hub and Mid Drive motors. In this guide we will talk about not only about each motor but weigh the Pros and Cons. Each motor system offers benefits for different riders. The best eBike motor is the one that is the best for your riding needs.
In This Guide:
- How Motors Work With eBikes: There are two types of sensors that manage the the electric assist.
- Different Types of Motors: There are two types of electric bike motors: Hub and Mid Drive.
- Hub Motors: There are two types of Hub Motors, Geared and Gearless, located at the center of either the front or rear wheel.
- Mid Drive Motors Located between your cranks, the motor spins a shaft connected to the chain ring.
- Which Motor is Best? Weighing the Pro’s and Con’s, there is a best motor for every rider.
- Other important considerations: Choosing the right motor for your type of riding.
How Electric Bike Motors with eBikes:
The basics of an electric bike motor is that it converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Easier said, the electric motor transfers that electric energy into mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is seen by the spinning of the wheel on a hub drive, or the spinning of the chain ring on a mid drive.
To manage the power output of electric bike motors, there are two main sensors used with the controller. A cadence sensor (or speed sensor) and a torque sensor.
A cadence sensor registers the RPM or speed of the wheel to apply the electric assist relative to the Pedal Assist mode that is selected, e.g. 1-5 or Eco, Tour, Sport, Turbo.
A torque sensor manages the Pedal Assist output of the motor by registering the amount of torque being applied through the pedals.
These two types of sensors are used differently in both hub and mid drive motors. Hub drive motors typically use cadence sensors, while mid drive motors use torque sensors. The difference in these sensors is noticeable between both motor types, which weighs into deciding which eBike motor is best for you.
Different Types of Electric Bike Motors:
When it comes to electric bikes, they all use the same basic components. They all have a motor, a controller, and a battery. Beyond that, there are some necessary sensors and other technology that help them function. The type of motor, controller, or battery are all determining factors in the capabilities of an electric bike.
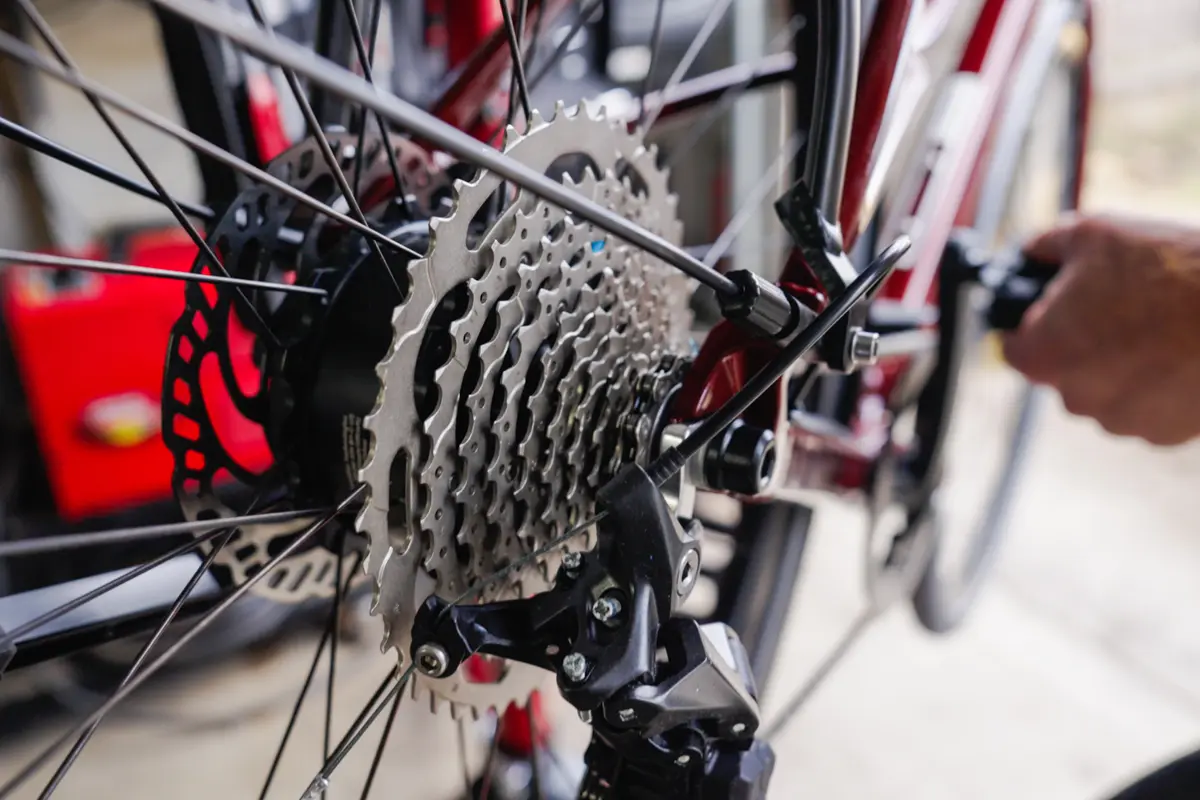
Hub motors are located in either the front or rear wheel, becoming the hub of the wheel itself.
Mid Drive Motors are located in the middle of the bike, attached to the frame, between the pedals. As seen on the Orbea Kemen
Hub Motors:
Hub drive motors have been around for the longest amount of time, with two types of hub motors available. Gearless (or Direct Drive) and Geared hub motors. Located in the wheel, the motor attaches to the frame of the bike using an axle. The motor being attached to the entire wheel itself spins around the axle creating the electric assist.
Hub drive motors have little to no moving parts which makes them extremely durable and relatively maintenance free. If damage to the motor happens, they are more budget friendly and more cost effective to replace the whole unit than try to repair it. Since the introduction of hub drive motors for electric bikes, they have made most of their identity in urban style bikes. Although they can be found in other types of bikes over the last few years, their affordability and low maintenance have made them ideal for commuters and recreational riders for years. With many manufacturers and a broad range of available motor sizes for power, there are class I, II, and III, hub drive motors available. Class II hub drive eBikes have a thumb throttle for electric assist when you aren’t pedaling. This is a nice feature if you ever brake a chain. The motor functions separately from your drivetrain and will allow you to ride it with use of the throttle as long as their is battery available.
Gearless, or Direct Drive Hub Motors
Direct Drive hub motors are the original and most basic electric motors used on eBikes. With no moving parts aside from the bearings it sits on, the motor directly spins around the axle. Direct drive motors tend to be larger than geared hub motors and they are able to maintain high RPM outputs. Due to their size and weight, they require more torque to propel them forward, which requires more battery storage if looking for adequate range. Direct Drive motors are capable of regenerative braking, and although it is a minimal amount of energy, the benefits can be seen on long descents. However, this is not enough energy regeneration to be noticed on daily commutes around town. Direct Drive motors with their high RPM and high top-speed abilities are popular for eMoped style electric bikes meant to be fun and go fast.
Geared Hub Motors
Geared hub motors work the same as Direct Drive motors, with the exception of using a series of gears within the hub to reduce the RPM’s of the motor to create more torque. This allows for more power at lower speeds, great for stop and go traffic, but reduces the overall top speeds seen with a Direct Drive motor.
Geared hub motors are smaller then Direct Drive motors. Having an internal series of gears, they require a smaller motor to generate the same amount of torque for the electric assist. Additionally, geared hub motors have a freewheel where the chain or belt connects to the hub. This allows the hub to spin freely when coasting. With the lack of engagement on the hub, geared hub motors are not capable of regenerative braking, but they will not have motor drag as seen Direct Drive motors. Along with size and more torque, the affordability of Geared hub motors has made them competitive contenders for not only urban eBikes, but touring, trekking, fat tire and cargo eBikes as well.
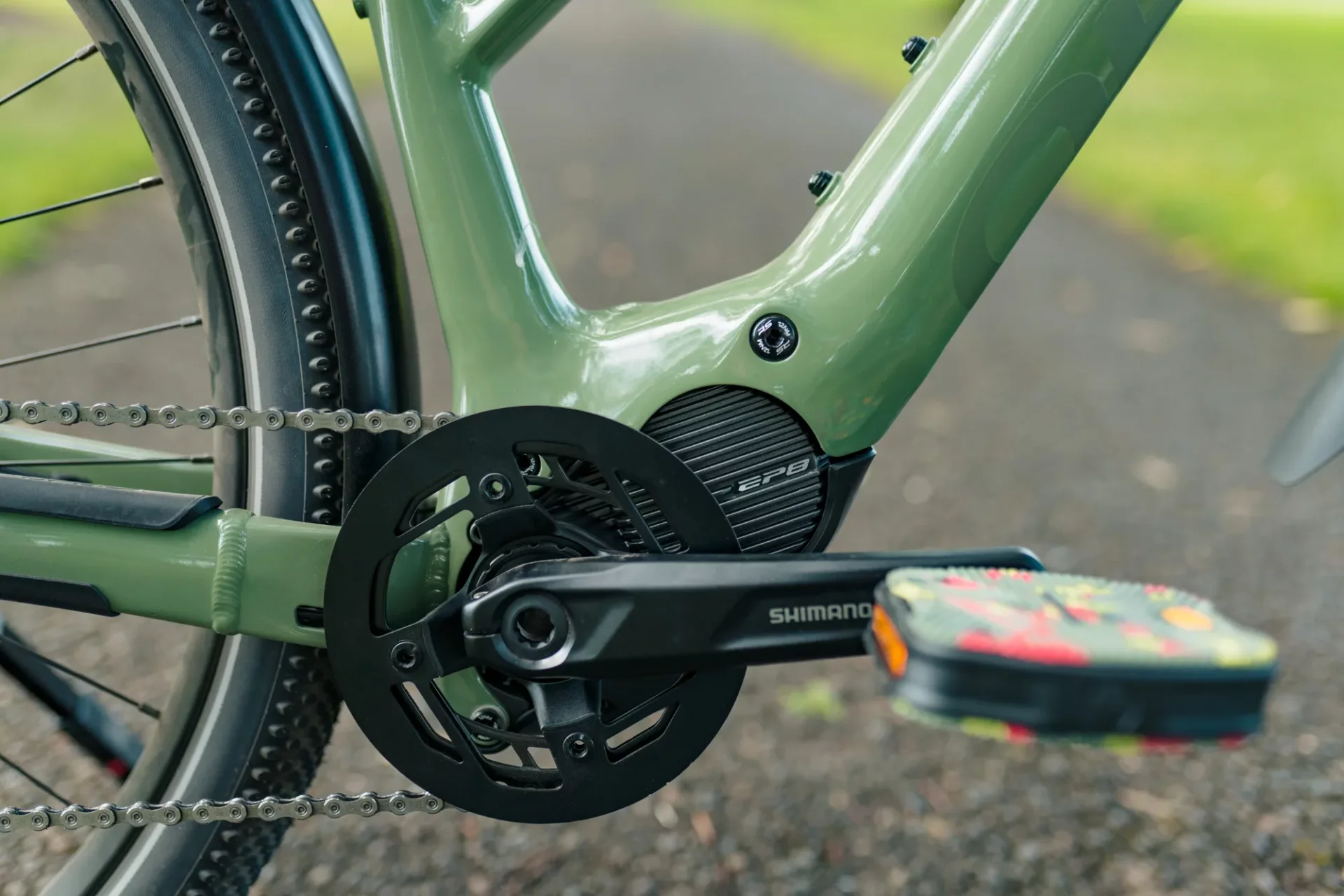
Mid Drive Motors:
Mid drive motors are mounted on the frame in the middle of the bike, replacing the bottom bracket. Mid drive motors use a series of gears within the motor to generate torque that spins a shaft connected to the chain ring. There are many benefits of this system, the motor is able to use gear reduction within the motor to reduce the RPM’s at the shaft for a higher torque output. This optimizes the performance of the motor and keeps a comfortable pedaling cadence for the rider.
Additionally, a mid drive motor is able to further optimize the efficiency of an electric bike by using the drivetrains gears, whether that be with a derailleur and cassette or an internally geared rear hub. The higher torque output and efficiency have made the mid drive motor of choice for electric mountain bikes and other performance focused eBikes, offering superior electric assist on steeper terrain. The torque sensor on Mid Drive eBikes also provides a more natural pedaling feel, which is important to cycling enthusiasts who are seeking electric assist without losing the pedaling feel of a non electric bike.

Which Motor is Best?
When weighing the Pros and Cons of Hub vs. Mid drive motors, the best motor ultimately depends on the application of the eBike. Although Mid Drive motors are highly desirable for performance eBikes like eMTB’s, the dependability and affordability of a Hub motor have made them the most popular for Urban eBikes.
Maintenance is a figurehead consideration for any electric bike motor. Hub drive motors require little to no maintenance due to minimal moving parts, and when maintenance may be required it is significantly more affordable.
Motor efficiency is likely the most important consideration regarding an eBike system. Battery size, motor size, and how that motor manages the power output. Although a high powered (Watts) hub motor with a throttle is fast and fun, it requires a lot of energy (large battery) to propel you forward. Mid drive motors have a smaller overall power output in Watts, but deliver high Torque outputs. Working with the bike’s drivetrain, a Mid Drive motor requires less energy (smaller battery) for the electric assist.
Hub Motors
Pros
- Essentially Maintenance Free
- Highly affordable
- Many options available
- Direct Drive offers high top speeds
- Thumb throttles are available
- Functions independently of the drivetrain allowing it to be rideable even with a broken chain
Cons
- Efficiency, requires more battery power to operate
- Heavy and throw off the center balance of the bike
- Can fail easily due to sustained power output and overheating
- Cadence sensor has an unnatural pedaling feel when engaging the motor
Mid Drive Motors
Pros
- Efficient, using the bikes gears allows for the motor to optimize its power consumption
- Motor location keeps the bike feeling balanced between the wheels
- Higher torque outputs, ideal for steep terrain and heavy loads
- Manages heat better for more strenuous sustained use
- Torque sensor makes a more natural pedaling feel when engaging the motor
- Rear wheel maintenance is unaffected by the motor
Cons
- Lower top speeds
- Functions directly with the drivetrain, if a chain or belt breaks, there is no way to continue to ride
- The motor is more complex, and more expensive to repair or replace

Other Important Considerations:
There are many factors to consider regarding choosing the best eBike motor system for your type of riding. From performance to purely fast, each motor offers something different for the rider.
When considering your next electric bike there are more things to consider then the motor type itself.
- Battery size for the appropriate range you are looking to get. Does that motor system accommodate accessories, lights, USB charging, things you may need to be better equipped on the road.
- Overall weight and size, regardless of the motor type are you able to transport the bike if the battery dies, or if you have to navigate any stairs to safely store it when not riding?
- Affordability, from initial investment to maintenance and repairs, consider an eBike that fits your long term budget.
Ultimately the deciding factor of which eBike motor is best is up to each rider. We tend to favor mid drive eBikes for their performance benefits, but understand the value and larger availability of hub drive eBikes.






[…] type of motor on your e-bike plays a significant role in determining […]
[…] using the e-bike for commuting, a motor optimized for efficiency might be preferable. Matching the motor’s capabilities with your riding needs ensures a satisfying […]
[…] These motors are beasts when it comes to off-roading, giving riders an electric boost right when the going gets tough. Plunked in the middle of the bike, mid-drive motors pack a punch by driving torque through chunky gears, spinning that chainring like a pro. This makes them perfect for eMTBs and anyone looking to conquer the outdoors without breaking a sweat (Electric Bike Journal). […]